Research shows the value of milk quality and udder health training
Explaining the "why" is critically important for workersDr. Zelmar Rodriguez, assistant professor in the Department of Large Animal Clinical Science at Michigan State University, conducted research showing that training of farm workers generates knowledge, satisfaction and a willingness to adhere to milking protocols resulting in quantifiably better milk quality, food safety and udder health.
Dr. Rodriguez shares the research findings:
Summary
Following an appropriate milking routine has a profound effect on reducing mastitis and improving food safety and milk quality. Our research has shown that training of farm workers generates knowledge, satisfaction and a willingness to adhere to milking protocols resulting in quantifiably better milk quality, food safety and udder health.
Milking routine in the context of milk quality and udder health
Clinical and subclinical mastitis are among the costliest diseases in dairy farming given their negative effect on milk quality and milk yield, ultimately affecting profitability of the dairy. Among the several procedures occurring on a dairy farm, there are very few with a more profound effect on reducing mastitis and improving food safety and milk quality than an appropriate milking routine. Multiple studies have evaluated each of the recommended steps of the standard milking routine reporting overwhelming benefits. Nevertheless, the variability in milk quality among dairy farms may be partly explained by poor protocol compliance.
Training as a milking routine limitation
Based on my experience, an important limitation to effectively following a milking routine by farm personnel is the lack of understanding of the reasons behind and importance of this essential part of the milking process. In other words, people need to know why they have to do what they have been told to do.
Multiple studies underscore the positive impact of training programs on various aspects of dairy farm operations which ultimately results in a positive return on equity. While there is no “one-size-fits-all” solution for mastitis management procedures, general training tailored to the specific needs of the farm may be impactful. However, there is limited follow up assessment of milking routine training program effectiveness to achieve improved protocol compliance and udder health on dairy farms.
Evaluating the impact of training - Research at MSU
Therefore, together with Dr. Pamela Ruegg from MSU and Drs. Mario Lopez and Marianna Gentilini from DeLaval, we carried out an experimental study to address the following questions:
- What is the current knowledge of farm workers about milking routines and how much can they learn about it?
- What is the impact of training farm workers on milking procedure compliance, udder health and milk quality?
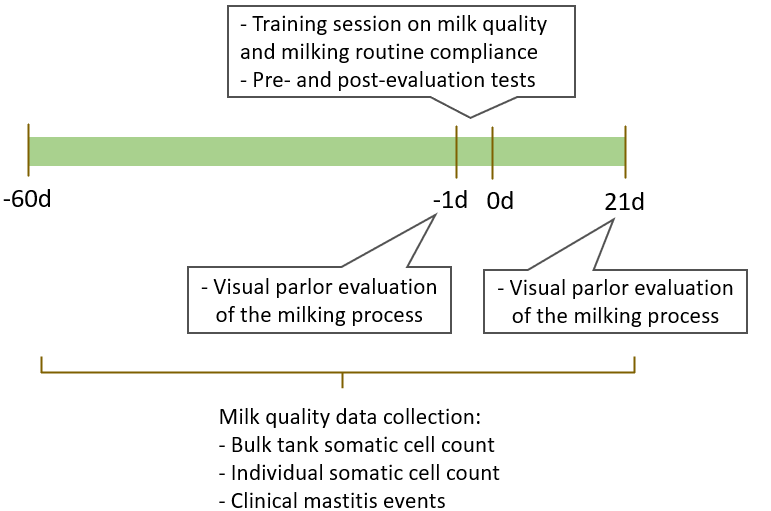
From April to September 2023, I visited 16 dairy farms, three times each. The initial visit involved a visual parlor evaluation, the second visit was to deliver a bilingual training session on milk quality and milking routine compliance, and the final visit was to conduct a post training parlor evaluation (Fig. 1). The parlor evaluations included recording pre-milking preparation times, such as contact time of pre-milking teat disinfectant, stimulation time, and milking time, along with assessing parlor and operator performance.
The training session (~ 1 hour) covered the pathogenesis, identification and risk factors of mastitis, and the reasons for each of the steps used in the milking routine on that particular farm. The milking routine was discussed, and any necessary adjustments were agreed upon by workers and employers during the training session based on the first parlor evaluation. All participants took voluntary and anonymous pre- and post-evaluation tests with 10 questions each, completed socio-demographic questions, and rated their level of satisfaction with the training material.
Through this article, I will highlight the most relevant results from this research:
1) Dairy workers participating in the study mirrored the national dairy workforce
The study involved 112 farm workers from 16 dairy farms who care for 17,205 cows. All farms had parallel or herringbone parlors. The median herd size was 1,101 cows and ranged from 280 to 2,330 lactating cows. The average number of employees was 15, ranging from 8 to 32.
The sociodemographic information of participants largely reflected national trends in the dairy farm workforce, suggesting a good generalizability of our findings. Specific results included:
- 75% of participants spoke Spanish, highlighting the importance of considering language barriers in training programs.
- The diverse educational background of workers represents a challenge for educators when generating training content for all participants.
- 70% of employees have less than 1 year of experience, likely related with the 33% turnover during the previous year (ranging from 0% to 125%) in the participating farms. Considering the limited experience by most employees, training workers to understand the milking protocol became crucial to achieving optimal milking performance.
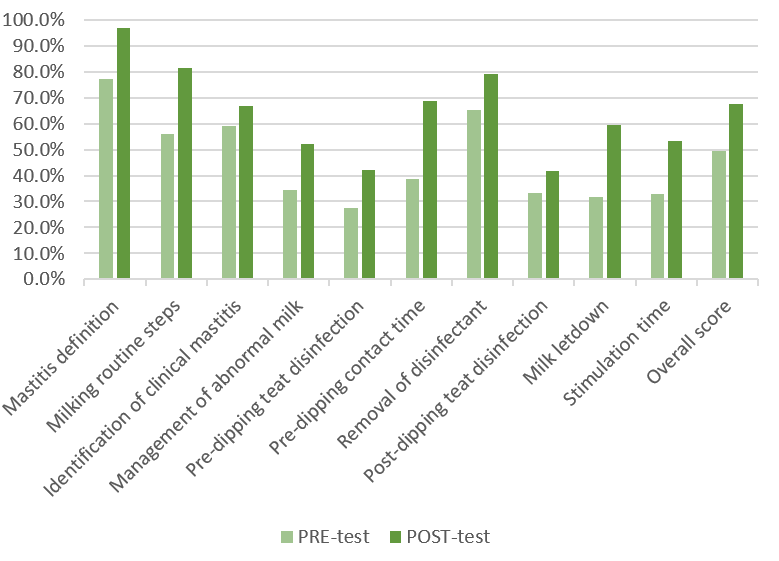
2) Dairy workers gained knowledge on the reasons and importance of adhering to the milking routine on their farms
- As compared to pre-test scores, dairy worker knowledge of the milking routine increased by 18% (Fig. 2), on average.
- During group discussions, milking technicians, managers and owners had the opportunity to reach consensus on various topics. For instance, they clarified procedures for managing abnormal milk, particularly in mild clinical cases.
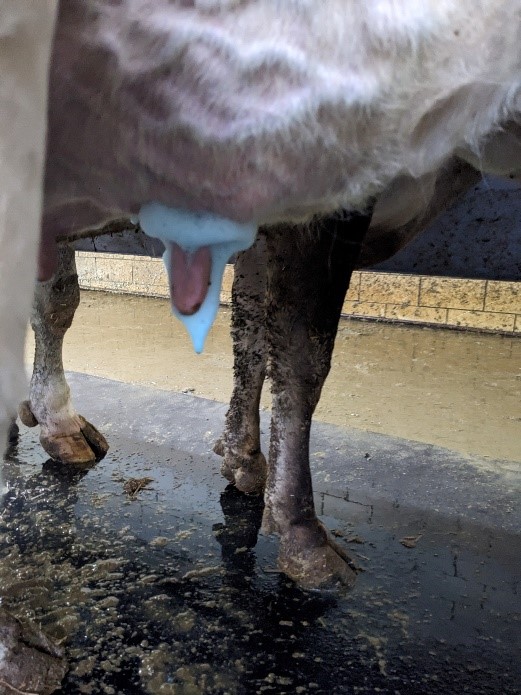
- The least clear topic was the importance and function of pre-milking teat disinfection (Fig. 3-4) followed by concepts related to milk letdown. However, there was substantial improvement in both topics after training (Fig. 2).
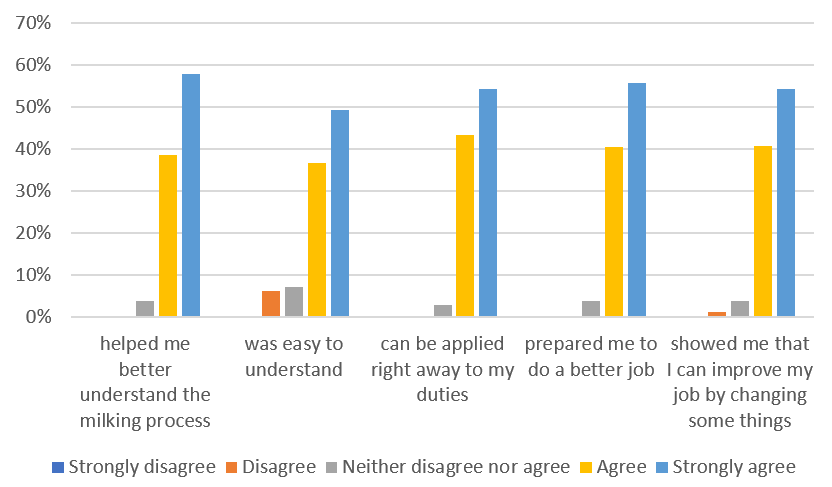
- Employees rated the training as highly beneficial (average score 4.5 out of 5) in terms of improving their understanding of the milking process, ease of comprehension, and immediate practical applicability in the field (Fig. 5).
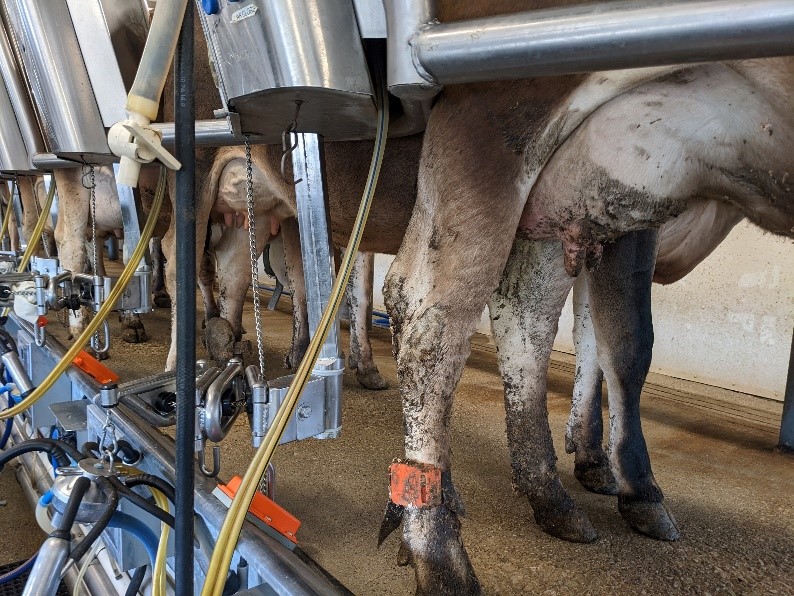


3) The training session generated a positive impact in milking routine compliance, milk quality and udder health
More time-effective parlor procedures were achieved after the training session. Main findings:
- Inadequate preparation time decreased from 41% of cows before training to 16% after training.
- Insufficient teat coverage decreased from 9.8% before training to 5.9% after training.
- Average stimulation time was reduced to 105 seconds/cow (target between 60 to 180 seconds).
- Pre-milking teat disinfection contact time increased 9 seconds/cow (recommendation is > 30 seconds).
- Milking time was reduced 25 seconds, likely due to reinforcement during training on avoiding unnecessary reattachment, and special attention if reattachments are set in manual.
There was improvement in milk quality and mastitis identification. The main findings were:
- Bulk tank somatic cell counts after training stopped the seasonal increasing trend during the 21 days after intervention.
- An increased number of clinical mastitis cases were recorded during the week after the training, likely because of reinforcement of forestripping as the best method to identify clinical mastitis.
Key takeaways
Training of farm workers generates knowledge, satisfaction, and a willingness to adhere to the milking protocol, resulting in quantifiably better milk quality and udder health. Thus, investing in having a well-trained workforce in your dairy will result in better job performance and increased job satisfaction.
MSU Extension educators are available to provide on-farm training for employees throughout Michigan, covering multiple areas of dairy management both in English and Spanish. Educational resources, event information, and list of dairy experts are shared through the MSU Extension dairy website.
This article was published by Michigan State University Extension.